High-Availability Cloud Hosting Architecture
Load balancing is essential for high-traffic websites to avoid overloading the connected resources. Businesses can achieve greater use of resources and decrease computing time. If your business involves large amounts of data processing and transfer, the benefits of load balancing are numerous.
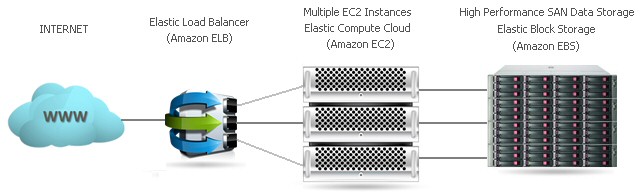
Multiple Cloud Instances with the same function is the base of a "Load Balancing Cluster". To distribute the user requests to Multiple Instances, a load balancer is useful. The load balancer checks the utilization of all the instances on the cloud and the instance with the estimated best performance will get the next user request. This algorithm ensures the best performance available at the time is given to the users.
High Performance SAN Data Storage
The Storage Area Network (SAN) is a highly scalable and fault tolerant central network storage cluster for your critical data on the Cloud Infrastructure. The SAN Data Storage connects directly to your Cloud Instance using extremely fast low latency Gigabit Ethernet connections. This allows customers to store data sequentially, or in parallel, without affecting the performance of the Cloud Instance. The SAN Data Storage is designed with multiple redundant enterprise class disk arrays for maximum protection and reliability of your critical data.
The Storage Area Network (SAN) is a highly scalable and fault tolerant central network storage cluster for your critical data on the Cloud Infrastructure. The SAN Data Storage connects directly to your Cloud Instance using extremely fast low latency Gigabit Ethernet connections. This allows customers to store data sequentially, or in parallel, without affecting the performance of the Cloud Instance. The SAN Data Storage is designed with multiple redundant enterprise class disk arrays for maximum protection and reliability of your critical data.
Geographic Failover Cloud Hosting
Geographical failover is a redundant system that is made to survive disruptions that can involve whole regions. Geographical failover eliminates certain weaknesses inherent to natural disasters, man-made disasters, mistakes, and law enforcement orders. Failover is a mechanism that ensures service continuity whereby single-point failures are eliminated. It is a mechanism because failover has to be minutiously designed, implemented, and deployed. There are several types of failover mechanisms but the most resilient configuration spans geographical locations.
Geographical failover is a redundant system that is made to survive disruptions that can involve whole regions. Geographical failover eliminates certain weaknesses inherent to natural disasters, man-made disasters, mistakes, and law enforcement orders. Failover is a mechanism that ensures service continuity whereby single-point failures are eliminated. It is a mechanism because failover has to be minutiously designed, implemented, and deployed. There are several types of failover mechanisms but the most resilient configuration spans geographical locations.
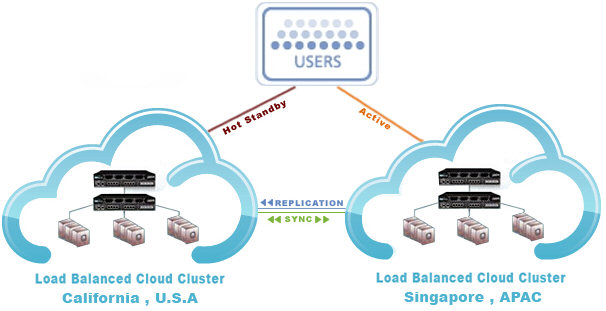
Traditionally, however, failover is implemented at the network level of the
infrastructure to prevent network disruptions. But in reality, there are several
elements of an infrastructure that could experience disruption. To avoid
disruption, the first cloud instance acts as the Primary Network in one
geographical location, and during normal usage it serves all requests. In the
event of a failure the Second Network, or Failover Cloud Instance becomes active
automatically in a different geographical location and serves all requests. The
data from the Primary cloud instance to the Failover cloud instance is
automatically synchronized on a daily basis. Both the Primary and Failover
instances are maintained by identical softwares, and all user specific data is
synchronized automatically.